Open-Loop Control Systems.
Those systems in which the output has noeffect on the control action are called open-loop control systems
Closed-Loop Control Systems.
Feedback control systems are often referred to as closed-loop control systems.In a closed-loop control system the actuating error signal, which is the difference between the input signal and the feedback signal(which may be the output signal itself or a function of the output signal and its derivatives and/or integrals), is fed to the controller so as to reduce the error and bring the output of the system to a desired value.
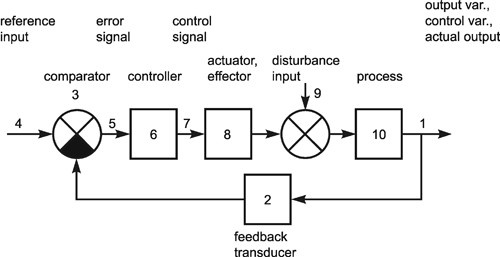 |
| CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL SYSTEM |
Advantages of Open Loop
- Less expensive than a corresponding closed-loop system.
- There is no stability problem.
- Convenient when output is hard to measure or measuring the output precisely is economically not feasible.
Disadvantages of Open Loop
- Disturbances and changes in calibration cause errors,and the output may be different from what is desired.
- To maintain the required quality in the output,recalibration is necessary from time to time.
- They are less accurate.
- If external disturbances are present, output differs significantly from the desired value.
TERMS USED IN CONTROL PROCESS
- Variable Process - proses pembolehubah
- Servo Controlled -pengawal serbo
- Feedback -suap balik
- Process -proses
- Set Point -titik mula
- Error -ralat
- Controller -pengawal
- Measurement -pengukuran